The transport layer is the fourth layer of the OSI model. For moving information between networked computers, the OSI layers are given a responsibility or group of responsibilities for each of the seven layers.
The transport layer facilitates the communication between application processes running on various hosts within a layered architecture of protocols and other network components. That is, the transport layer takes data sent at the session layer and divides the data into segments on the transmitting end, and reassembles the segments on the receiving end converting them back into data that the session layer may use. Flow control is handled by the transport layer. It provides data at a pace that matches the receiving device’s connection speed, and error control, determining if the data was received with errors and thus requesting again. The Transmission Control Protocol(TCP) is the best example of a Transport Layer.
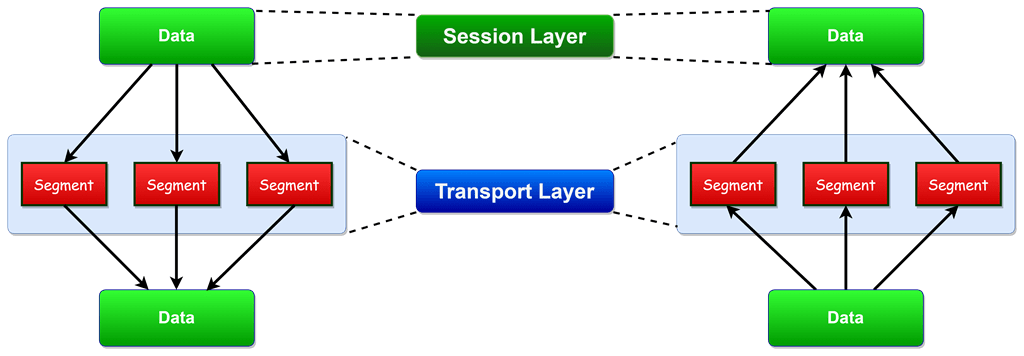
Functions of Transport Layer
Segmentation and Reassembly
The transport layer receives the data from the Session Layer and then separates that data into small units called segments.
Each segment created has a header attached to it. The data is reassembled at the destination station by the transport layer.
Service Point Addressing
The transport layer header provides a form of address known as a service point address or port address in order to deliver the message to the relevant process. The transport layer ensures that the message is delivered to the relevant process by identifying this address.
Services of Transport Layer
Connection-Oriented Communication
Before data is transmitted, devices at the end-points of a network communication establish a handshake protocol such as TCP to ensure the connection is stable. The disadvantage of this system is that an acknowledgment is required for each delivered message, which adds a significant network burden when compared to self-correcting packets. When incorrect byte streams or datagrams are delivered, the network performance is significantly slowed.
Same Order Delivery
By giving a number to each packet, it makes sure that they are always sent in exact sequence. Although the network layer is in charge, the transport layer can correct any sequence mismatches caused by packet losses or device interruptions by rearranging them.
Data Integrity
Checksums are used to assure data integrity across all delivery tiers. These checksums ensure that the data supplied is identical to the data received and is not corrupt. By requesting retransmission from other layers, missing or damaged data can be reissued.
Flow Control
Manages data flow to guarantee that data is provided at a rate that is acceptable to both parties that is sender, and receiver.
Traffic Control
The data traffic due to bandwidth and processing speed restrictions have an impact on practically every aspect of a network, therefore transport layer can detect the signs of overloaded nodes and lower flow rates and take corrective measures.
Multiplexing
Simultaneous application use is allowed over a network like opening different web browsers on the same computer. Multiplexing is handled in the service layer.
Byte orientation
The transport layer permits the transmission of byte-oriented data streams instead of packets.







0 Comments